Becoming a Nuclear Medicine Technologist: Your Complete Guide
Explore the educational requirements, certification process, and job outlook for aspiring nuclear medicine technologists. Learn more here.
"Becoming a Nuclear Medicine Technologist: Your Complete Guide"
Exploring the Role of Nuclear Medicine Technologists in Healthcare
In the dynamic field of healthcare, nuclear medicine technologists play a vital role in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions using radioactive substances. These highly skilled professionals operate specialized equipment to perform imaging procedures and administer radiopharmaceuticals, contributing to the delivery of accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. In this article, we'll delve into the responsibilities, training, and significance of nuclear medicine technologists in the healthcare industry.
Role and Responsibilities
Nuclear medicine technologists are responsible for conducting a range of diagnostic procedures and therapeutic interventions using radioactive materials. Their primary duties include:
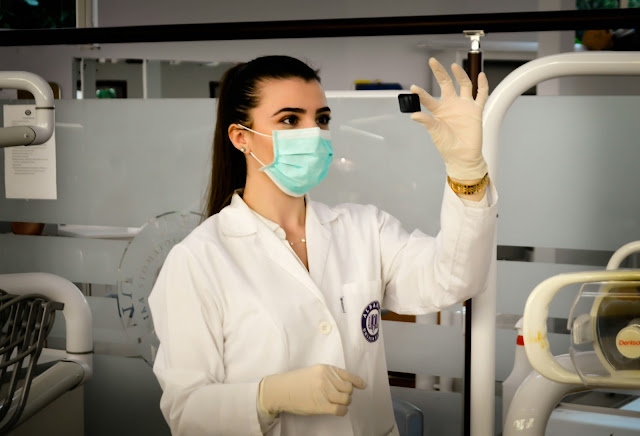
Patient Preparation: Nuclear medicine technologists prepare patients for imaging procedures by explaining the process, obtaining medical histories, and addressing any concerns or questions.
Radiopharmaceutical Administration: They administer radiopharmaceuticals to patients orally, intravenously, or through other routes, ensuring proper dosage and patient safety.
Imaging Procedures: Nuclear medicine technologists operate specialized imaging equipment, such as gamma cameras and PET scanners, to capture images of the body's internal organs and tissues. These images provide valuable information about physiological functions and disease processes.
Data Analysis: After acquiring images, technologists analyze and interpret the results to identify abnormalities or areas of interest. They collaborate with radiologists and other healthcare professionals to generate accurate diagnostic reports.
Quality Control: Technologists perform quality control checks on equipment and radioactive materials to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards.
Patient Care and Safety: Throughout the imaging process, technologists prioritize patient comfort and safety, adhering to radiation safety protocols and minimizing radiation exposure risks.
Training and Education
Becoming a nuclear medicine technologist typically requires a combination of academic coursework and clinical training. Most technologists hold an associate or bachelor's degree in nuclear medicine technology or a related field. Academic programs cover topics such as radiation physics, radiopharmacy, anatomy, physiology, and medical imaging techniques.
In addition to formal education, aspiring nuclear medicine technologists undergo clinical rotations or internships to gain hands-on experience in performing imaging procedures and working with patients under the supervision of licensed professionals. After completing their education and training, technologists may pursue certification through organizations such as the Nuclear Medicine Technology Certification Board (NMTCB) or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
Significance in Healthcare
Nuclear medicine technologists play a crucial role in modern healthcare by providing valuable diagnostic information that helps clinicians detect and manage a wide range of medical conditions, including cancer, heart disease, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries. By performing imaging studies such as bone scans, PET scans, and myocardial perfusion imaging, technologists assist physicians in making informed decisions about patient care, treatment planning, and monitoring disease progression.
Furthermore, nuclear medicine technologists contribute to advancements in medical research and innovation by participating in clinical trials, conducting imaging studies for drug development, and collaborating with interdisciplinary teams to improve diagnostic techniques and therapeutic interventions.
In conclusion, nuclear medicine technologists play an integral role in the healthcare continuum, leveraging their expertise in radioactive imaging techniques to support accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and patient-centered care. With ongoing advancements in technology and healthcare delivery, the demand for skilled nuclear medicine technologists is expected to continue growing, ensuring their enduring impact on the field of medical imaging and patient outcomes.